Profit margin is a crucial financial metric that indicates the efficiency and profitability of a small business. In order to determine what constitutes a good profit margin for such enterprises, it is imperative to consider various factors that influence profitability. This article aims to provide an objective analysis of the different types of profit margins and their significance in the context of small businesses. By evaluating industry standards and offering strategies for improvement, this article will equip readers with the knowledge needed to achieve and maintain a healthy profit margin, fostering sustainable growth and success.
Key Takeaways
- Profit margins are affected by factors such as industry competition, pricing strategies, cost management, and economic conditions.
- Different types of profit margins, including gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, allow businesses to accurately assess their financial performance.
- Aligning profit margins with industry standards is important for generating revenue, covering costs, and assessing competitiveness.
- Strategies to improve profit margins include cost management, diversifying revenue streams, implementing marketing strategies, and aligning with industry benchmarks and best practices.
Factors Affecting Profit Margins
One important aspect to consider when evaluating profit margins for small businesses is the impact of various factors that can affect these margins. These factors can include industry competition, pricing strategies, cost management, and economic conditions. Industry competition plays a significant role in determining profit margins, as intense competition often leads to price wars and lower profit margins. Pricing strategies also have a direct impact on profit margins, with businesses setting prices based on market demand and cost structures.
Effective cost management is crucial for maintaining healthy profit margins since it helps control expenses and increase operational efficiency. Economic conditions such as inflation rates and interest rates can also influence profit margins by affecting consumer spending patterns and business costs. Therefore, understanding and adapting to these factors are essential for small businesses to achieve sustainable profit margins in their respective industries.
Understanding Different Types of Profit Margins
An essential aspect of understanding profit margins involves familiarizing oneself with the various types of profit margins. These different types provide insights into how a business generates and manages its profits. The three main types of profit margins are gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin.
- Gross Profit Margin: This measures the profitability of a company’s core operations by calculating the percentage of revenue left after deducting the cost of goods sold. It indicates how efficiently a business is managing its production costs.
- Operating Profit Margin: This ratio evaluates a company’s profitability from its normal business activities, excluding non-operating income and expenses. It highlights how well a business is generating profits from its day-to-day operations.
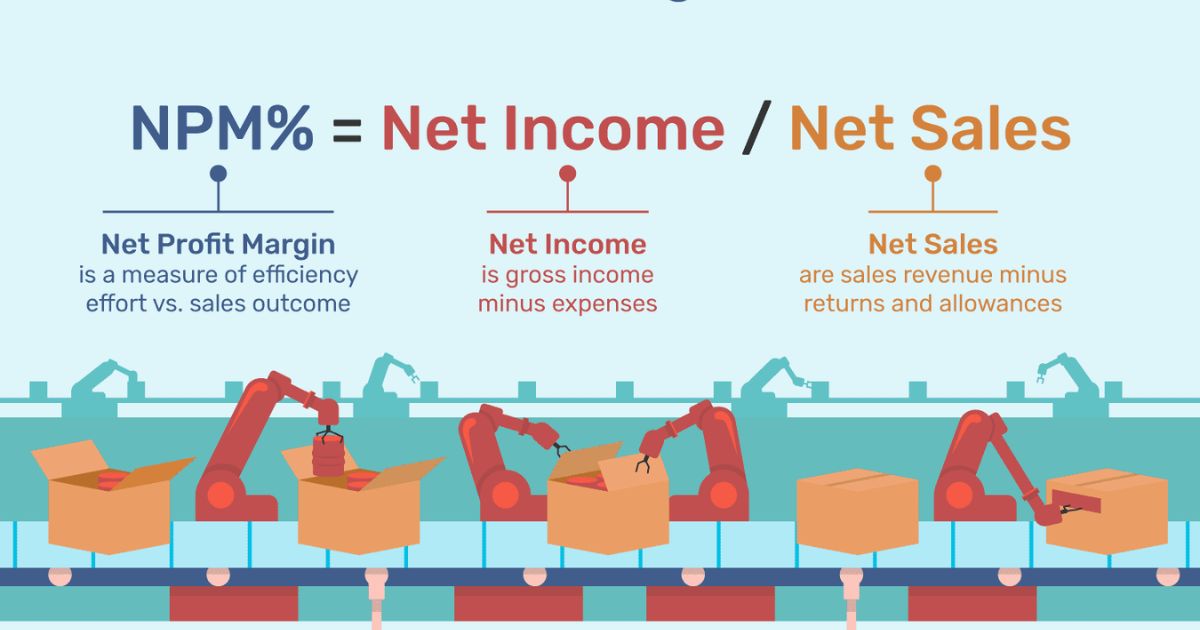
- Net Profit Margin: This metric represents the percentage of revenue that remains as net income after accounting for all expenses, including taxes and interest payments. It reflects the overall profitability and efficiency of a company.
Understanding these different types allows businesses to assess their financial performance accurately and make informed decisions to improve their profitability in an increasingly competitive market.
Determining a Good Profit Margin for Your Small Business
To evaluate the financial performance of a small enterprise, it is crucial to determine a profit margin that aligns with industry standards and ensures sustainability. A good profit margin signifies that a business is generating sufficient revenue to cover its costs and generate profits. The determination of what constitutes a good profit margin varies across industries. Analyzing industry data can provide valuable insights into typical profit margins for specific sectors.
For example, the average profit margin in the retail industry may differ significantly from that in the manufacturing sector. By comparing their own profit margin against industry benchmarks, small businesses can assess their competitiveness and identify areas for improvement. This analysis allows them to make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, cost control measures, and overall financial management.
In the subsequent section, we will delve deeper into analyzing industry standards for profit margins and explore how small businesses can utilize this information effectively to enhance their financial performance.
Analyzing Industry Standards for Profit Margins
Analyzing industry standards for profit margins involves examining data specific to various sectors, which can provide valuable insights into the financial performance of businesses. By comparing a small business’s profit margin to industry benchmarks, owners and managers can assess their company’s competitiveness and identify areas for improvement. Here are three key points to consider when analyzing industry standards for profit margins:
- Industry Variations: Profit margins vary across industries due to factors such as market demand, competition levels, and cost structures. For example, the retail sector typically has lower profit margins compared to technology companies.
- Size Matters: Profit margins may also differ based on the size of the business. Larger organizations often benefit from economies of scale and have higher profit margins than smaller enterprises.
- Historical Trends: Examining historical data allows businesses to track changes in profit margins over time and identify potential patterns or trends that might impact their own profitability.
Understanding these industry-specific benchmarks is crucial for small businesses seeking to gauge their financial performance accurately. In order to improve your small business’s profit margin, it is essential to implement effective strategies that align with your industry’s norms and best practices.
Strategies to Improve Your Small Business’s Profit Margin

Implementing effective strategies that align with industry benchmarks and best practices is crucial for improving the financial performance of small businesses. One such strategy is to focus on cost management and reduction. By identifying areas where costs can be minimized without compromising quality, small businesses can increase their profit margin. This can include negotiating better deals with suppliers, optimizing inventory levels, and streamlining operations.
Another strategy is to diversify revenue streams by expanding into new markets or offering additional products or services. By doing so, small businesses can reduce their reliance on a single source of income and increase their overall profitability. Additionally, implementing marketing strategies such as targeted advertising and customer retention programs can help attract new customers and boost sales. These strategies are essential for driving growth and maximizing profit margins in small businesses.
Transition Sentence: Evaluating the importance of profit margins for small businesses requires an understanding of how they impact financial stability and long-term success.
Evaluating the Importance of Profit Margins for Small Businesses
Evaluating the significance of profit margins in small businesses necessitates a comprehensive examination of their impact on financial stability and long-term viability. Profit margins serve as important indicators of a business’s overall health and success. Here are three key reasons why profit margins are crucial for small businesses:
- Financial Stability: Maintaining healthy profit margins ensures that a business has sufficient funds to cover its expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and weather economic downturns.
- Competitive Advantage: Higher profit margins enable small businesses to offer competitive prices, invest in quality products or services, and differentiate themselves from competitors.
- Long-Term Viability: Sustainable profit margins contribute to the long-term survival and growth of small businesses by providing resources for innovation, expansion into new markets, and attracting investment.
Tips to Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Profit Margin
To achieve and maintain a healthy profit margin, it is essential for businesses to carefully manage their pricing strategies. One effective tip is to conduct thorough market research to understand customer preferences and competitors’ pricing. This data-driven approach allows businesses to set prices that are competitive yet profitable. Additionally, implementing cost control measures can help reduce expenses and increase profitability. By analyzing operational costs, optimizing production processes, and negotiating favorable supplier contracts, businesses can improve their profit margins.
Another strategy is to focus on customer retention and upselling. Cultivating strong relationships with existing customers increases the likelihood of repeat purchases and higher average transaction values. Finally, regularly reviewing and adjusting pricing strategies based on market conditions ensures businesses remain competitive while maximizing profits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, determining a good profit margin for a small business is crucial for its success and sustainability. By analyzing industry standards and implementing strategies to improve profitability, small businesses can achieve and maintain a healthy profit margin. Profit margins play a significant role in evaluating the financial health of a business and are essential for long-term growth. It is imperative for small businesses to prioritize profitability and strive towards maximizing their profit margins. After all, the higher the profit margin, the greater the financial stability and potential for success.